|
|
Molluscs
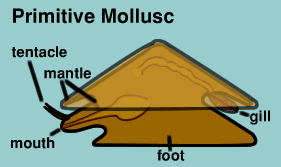
It is believed that modern molluscs evolved from a creature similar to the one above. It had its gills, reproductive organs and excretory organs within its mantle cavity at the rear of the animal. Although there are numerous limpet-like fossils which are of this structure, only one species has been brought up from 5,000 metres near the coast of Mexico in the pacific Ocean. It was first captured in 1957.
During development, a ll modern molluscs undergo torsion, where the mollusc body twists so that the mantle cavity, and the organs it holds, come to rest over the head, facing the incoming current.
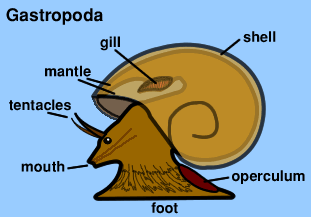
Some Molluscs groups which are featured in this intertidal web site are:
|
|
|
Chitons
False Limpets
Limpets
Top Shells
Nerites
Shell-less Molluscs
Turbans
Tritons
Murex Shells
Periwinkles & kin
Mussels
Siphon Shells
Bivalves
Home
Page
Taxonomy
Biogeography
Rocky Shores
Tidal Levels
Intertidal Zonation
Environmental Factors
Biological
Factors
Feeding Relationships
Activities
Glossary
References
| For more information on Molluscs visit MESA Molluscs |
 Life
on Australian Seashores
Life
on Australian Seashores
by Keith Davey (C) 2000
Learning Consultant
- Media
The University of Newcastle
email at australian_seashores@hotmail.com
Scientific Consultant: Phil
Colman
site created 01.01.98 : updated 01.04.2000